
C-Terminal Modification of Fully Unprotected Peptide Hydrazides via in Situ Generation of Isocyanates
C-Terminal Modification of Fully Unprotected Peptide Hydrazides via in Situ Generation of Isocyanates
Org. Lett., 2016, 18 (6), pp 1222–1225
DOI: 10.1021/acs.orglett.5b03625
Publication Date (Web): March 7, 2016
Alexander A. Vinogradov, Mark D. Simon, and Bradley L. Pentelute*
Abstract
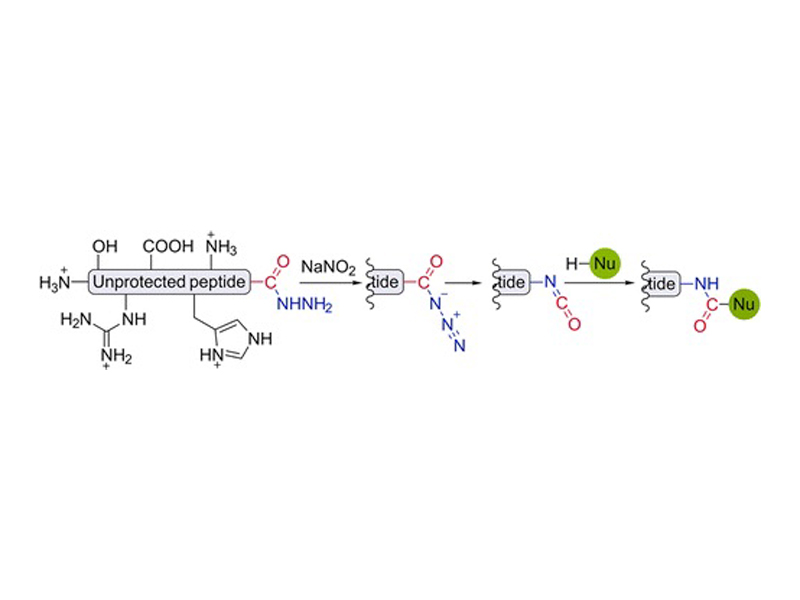
A method for chemo- and regioselective conjugation of nucleophiles to fully unprotected peptides and proteins via in situ generation of C-terminal isocyanates is reported. Oxidation of C-terminal peptide hydrazides in aqueous media followed by Curtius rearrangement of acyl azides reliably generates isocyanates, which react with a variety of external nucleophiles, such as hydrazines, hydrazides, aromatic thiols, and hydroxylamines. Multiple peptides and a 53 kDa protein hydrazide were conjugated to different nucleophiles using this reaction.



