
Selective N-Arylation of p-Aminophenylalanine in Unprotected Peptides with Organometallic Palladium Reagents
Selective N-Arylation of p-Aminophenylalanine in Unprotected Peptides with Organometallic Palladium Reagents
First published: 20 May 2021 https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202104780
Aaron J. Mallek,Prof. Bradley L. Pentelute,Prof. Stephen L. Buchwald
Abstract
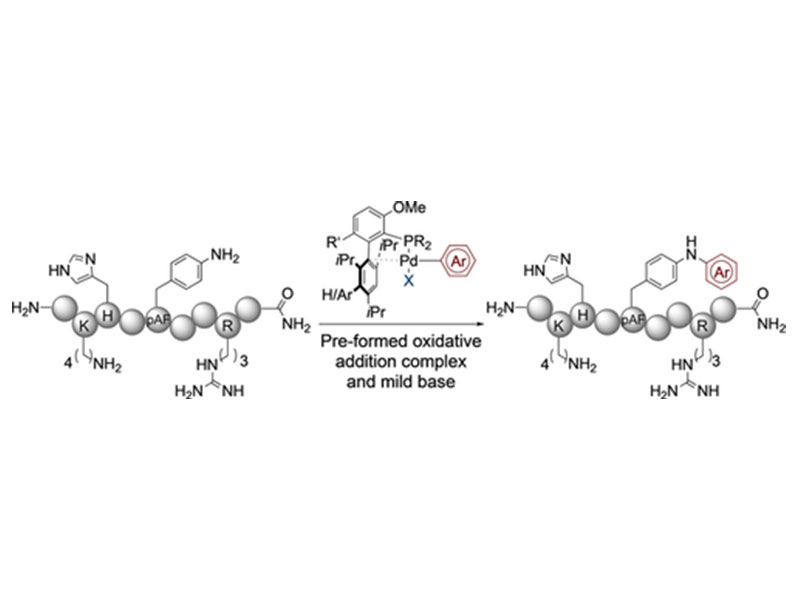
Pre-formed oxidative addition complexes (OACs) are utilized to selectively arylate p-aminophenylalanine (pAF) in the presence of native functional groups, except cysteine. In phosphate buffer pH 7.5, OACs derived from electron-poor arenes provide full conversion in as little as 2 hours at micromolar concentration. A complimentary procedure using the weak base 1,5-diazabicyclo(4.3.0)non-5-ene (DBN) is also presented enabling arylation with electron-rich substrates with up to 97 % conversion.



