
Engineering Bioactive Dimeric Transcription Factor Analogs via Palladium Rebound Reagents
Engineering Bioactive Dimeric Transcription Factor Analogs via Palladium Rebound Reagents
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 30, 11788–11798
Muhammad Jbara, Sebastian Pomplun, Carly K. Schissel, Susana Wilson Hawken, Ann Boija, Isaac Klein, Jacob Rodriguez, Stephen L. Buchwald, and Bradley L. Pentelute*
Abstract
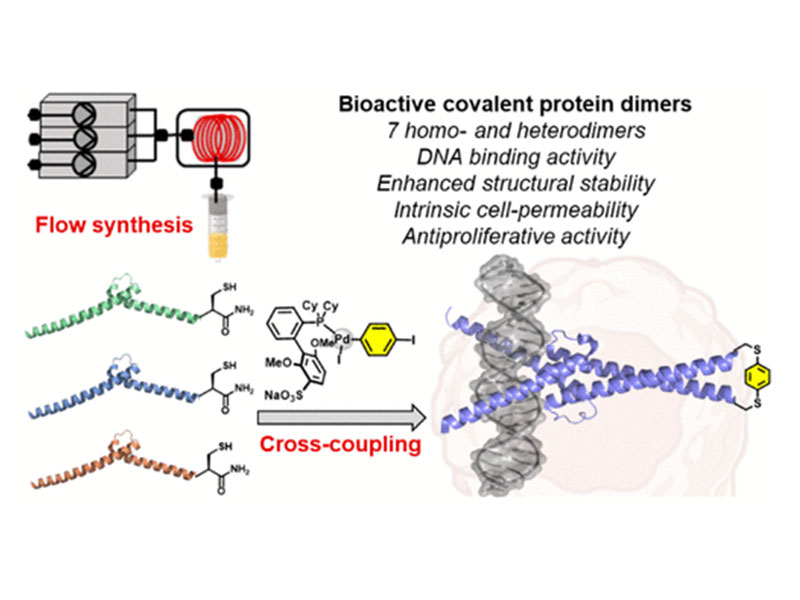
Transcription factors (TF), such as Myc, are proteins implicated in disease pathogenesis, with dysregulation of Myc expression in 50% of all human cancers. Still, targeting Myc remains a challenge due to the lack of small molecule binding pockets in the tertiary structure. Here, we report synthetic covalently linked TF mimetics that inhibit oncogenic Myc-driven transcription by antagonistic binding of the target DNA-binding site. We combined automated flow peptide chemistry with palladium(II) oxidative addition complexes (OACs) to engineer covalent protein dimers derived from the DNA-binding domains of Myc, Max, and Omomyc TF analogs. Palladium-mediated cross-coupling of synthesized protein monomers resulted in milligram quantities of seven different covalent homo- and heterodimers. The covalent helical dimers were found to bind DNA and exhibited improved thermal stability. Cell-based studies revealed the Max-Max covalent dimer is cell-penetrating and interfered with Myc-dependent gene transcription resulting in reduced cancer cell proliferation (EC50 of 6 μM in HeLa). RNA sequencing and gene analysis of extracted RNA from treated cancer cells confirmed that the covalent Max-Max homodimer interferes with Myc-dependent transcription. Flow chemistry, combined with palladium(II) OACs, has enabled a practical strategy to generate new bioactive compounds to inhibit tumor cell proliferation.



