
A perfluoroaromatic abiotic analog of H2 relaxin enabled by rapid flow-based peptide synthesis
A perfluoroaromatic abiotic analog of H2 relaxin enabled by rapid flow-based peptide synthesis
Org. Biomol. Chem., 2016,14, 3345-3349
Received 26 Jan 2016, Accepted 01 Mar 2016
First published online 04 Mar 2016
Tessa Lühmann, Surin K. Mong, Mark D. Simon, Lorenz Meinelb & Bradley L. Pentelute*
Abstract
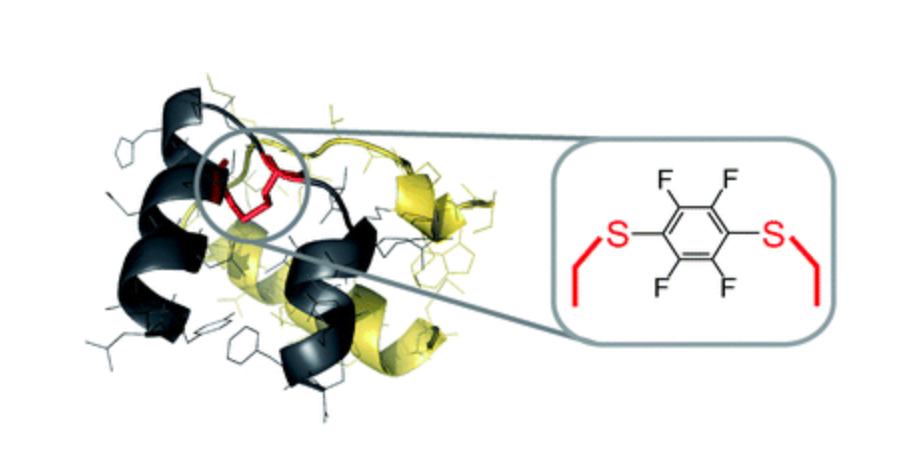
H2 relaxin is a pleiotropic peptide hormone with clinical potential. Here we report on the reaction and use of hexafluorobenzene as an intramolecular disulfide replacement between Cys10 and Cys15 in the A-chain of H2 relaxin. Using flow-based Fmoc solid-phase peptide synthesis methodology we were able to obtain high-quality H2 relaxin fragments that were previously reported as challenging to synthesize. Subsequent native chemical ligation and oxidative folding enabled total synthesis of both wild type H2 relaxin and a C6F4 linked analog. Cell-based activity assays revealed modest activity for the C6F4 linked H2 relaxin analog, albeit 100-fold reduced relative to wild type. This work demonstrates how perfluoroarylation-cysteine SNAr chemistry may be a useful tool for the selective replacement of native disulfide bonds in proteins.



