
pyBinder: Quantitation to Advance Affinity Selection-Mass Spectrometry
pyBinder: Quantitation to Advance Affinity Selection-Mass Spectrometry
Joseph S. Brown Michael A. Lee Wayne Vuong Andrei Loas Bradley L. Pentelute*
Abstract
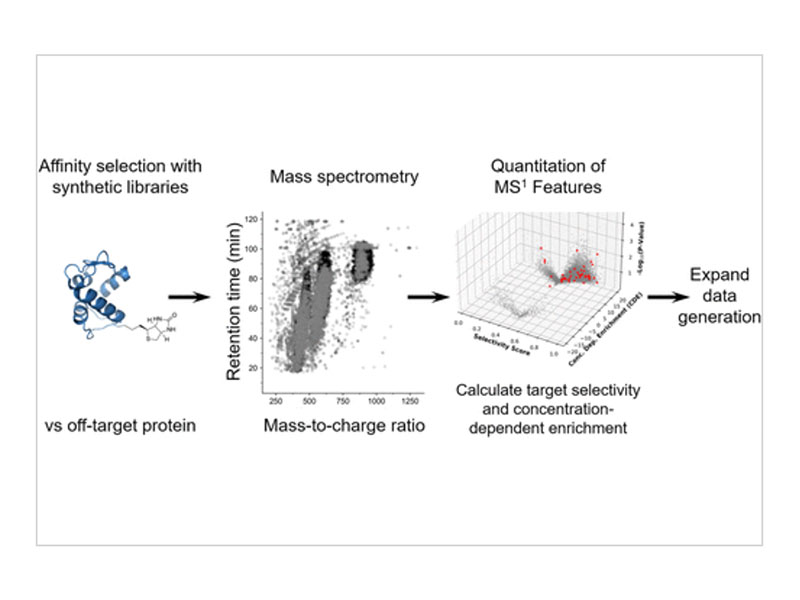
Affinity selection-mass spectrometry (AS-MS) is a ligand discovery platform that relies upon mass spectrometry to identify molecules bound to a biomolecular target. When utilized with large peptide libraries (108 members), AS-MS sample complexity can surpass the sequencing capacity of modern mass spectrometers, resulting in incomplete data, identification of few target-specific ligands, and/or incomplete sequencing. To address this challenge, we introduce pyBinder to perform quantitation on AS-MS data to process primary MS1 data and develop two scores to rank the peptides from the integration of their peak area: target selectivity and concentration-dependent enrichment. We benchmark pyBinder utilizing AS-MS data developed against antihemagglutinin antibody 12ca5, revealing that peptides that contain a motif known for target-specific high-affinity binding are well characterized by these two scores. AS-MS data from a second protein target, WD Repeat Domain 5 (WDR5), is analyzed to confirm the two pyBinder scores reliably capture the target-specific motif-containing peptides. From the results delivered by pyBinder, a list of target-selective features is developed and fed back into subsequent MS experiments to facilitate expanded data generation and the targeted discovery of selective ligands. pyBinder analysis resulted in a 4-fold increase in motif-containing sequence identification for WDR5 (from 3 to 14 ligands discovered), showing the utility of the two scores. This work establishes an improved approach for AS-MS to enable discovery outcomes (i.e., more ligands identified), but also a way to compare AS-MS data across samples, protocols, and conditions broadly.



