
Automated Flow Synthesis of Artificial Heme Enzymes for Enantiodivergent Biocatalysis
Automated Flow Synthesis of Artificial Heme Enzymes for Enantiodivergent Biocatalysis
Giulio Fittolani Dennis A. Kutateladze Andrei Loas Stephen L. Buchwald* Bradley L. Pentelute*
Abstract
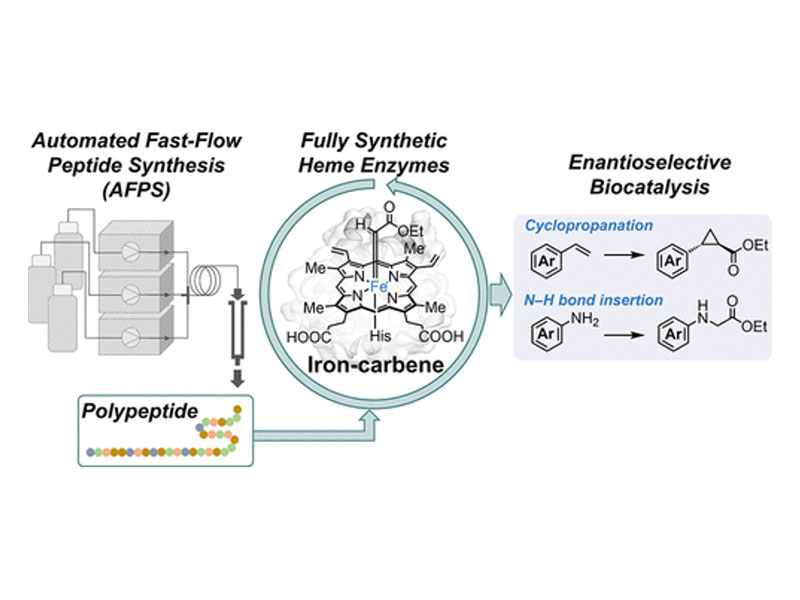
The remarkable efficiency with which enzymes catalyze small-molecule reactions has driven their widespread application in organic chemistry. Here, we employ automated fast-flow solid-phase synthesis to access catalytically active full-length enzymes without restrictions on the number and structure of noncanonical amino acids incorporated. We demonstrate the total syntheses of iron-dependent Bacillus subtilis myoglobin (BsMb) and sperm whale myoglobin (SwMb). The synthetic enzymes displayed excellent enantioselectivity and yield in carbene transfer reactions. Absolute control over enantioselectivity in styrene cyclopropanation was achieved using synthetic L- and D-BsMb mutants, which delivered each enantiomer of cyclopropane product in identical and opposite enantiomeric enrichment. BsMb mutants outfitted with noncanonical amino acids were used to facilitate detailed structure–activity relationship studies, revealing a previously unrecognized hydrogen-bonding interaction as the primary driver of enantioselectivity in styrene cyclopropanation. We anticipate that our approach will advance biocatalysis by providing reliable and rapid access to fully synthetic enzymes possessing noncanonical amino acids.



