
Rapid Production of Native and Mirror-Image Tumor Necrosis Factor-α Enabled by Automated Flow Peptide Synthesis Technology
Rapid Production of Native and Mirror-Image Tumor Necrosis Factor-α Enabled by Automated Flow Peptide Synthesis Technology
Ahmet Yesilcimen Alex J. Callahan Tara L. Travaline Satish Gandhesiri Olena S. Tokareva Andrei LoasJohn H. McGee*Bradley L. Pentelute*
Abstract
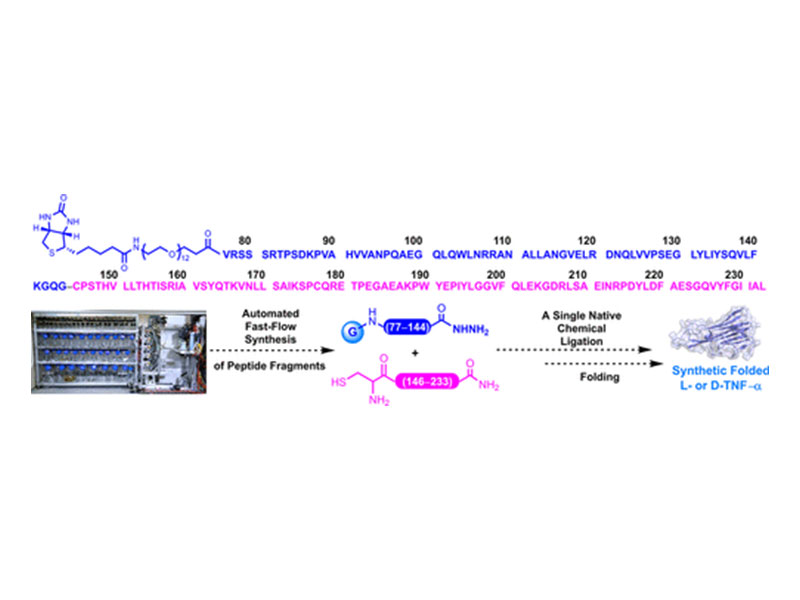
Tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) plays a central role in immune response regulation. Because elevated TNF-α production is correlated with a range of diseases, inhibiting the interaction of this protein with its native receptors has been thoroughly explored as a therapeutic avenue. Despite advancements in the development of TNF-α inhibitors, concerns remain regarding immunogenicity and loss of activity in vivo. To facilitate the discovery of stable and less immunogenic therapeutic modalities, we applied a single-shot automated fast-flow peptide synthesis (AFPS) strategy to produce full-length TNF-α, resulting in a complex reaction mixture. Leveraging the ability of AFPS to generate long peptides with high purity, we combined this technology with native chemical ligation (NCL). An NCL reaction using two fragments readily produced by AFPS afforded synthetic L- and D-TNF-α in milligram quantities (up to 5.5 mg, ∼28% yield). Following the oxidative folding of synthetic TNF-α using established conditions, higher molecular weight species were generated. Through high-throughput screening of refolding conditions, functional synthetic L- and mirror-image D-TNF-α were obtained, exhibiting characteristics analogous to those of the recombinant TNF-α. Overall, this approach can serve as a general protocol for accessing proteins that are intractable by modern protein synthesis methods, therefore, streamlining the development of novel therapeutics.



